Trial: Efficacy and Safety of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation as an Add-on Treatment for Bipolar Depression: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2018.
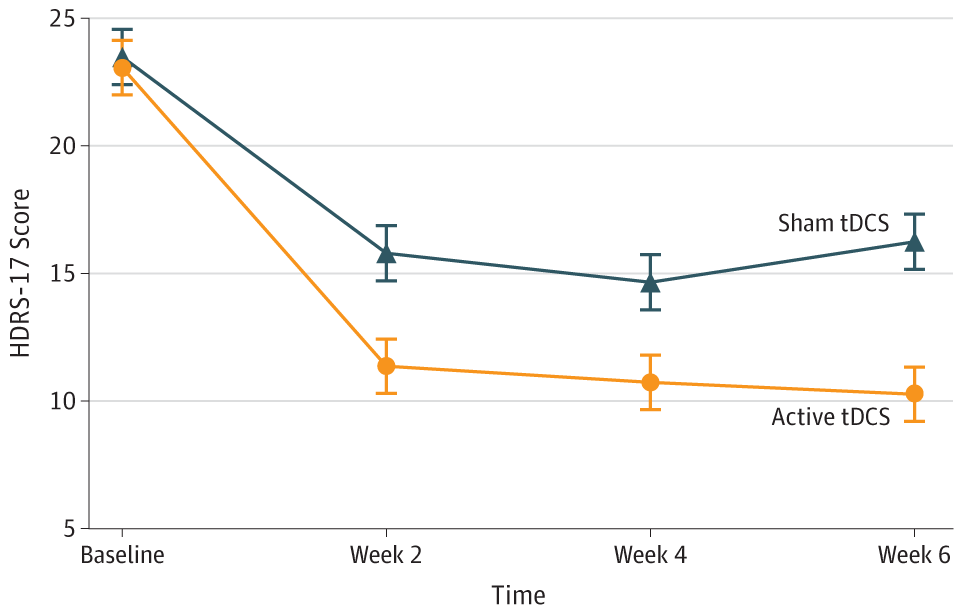
Design: Randomized, sham-controlled, double-blinded trial involving 59 patients aged between 18 to 65 years. Participants were diagnosed with either type I or type II bipolar disorder, were on stable pharmacologic regimen, had HDRS-17 score > 17, and were at low risk of suicide.
Intervention: 10 daily 30 minute sessions at 2 mA. Then 1 session every 2 weeks until week 6. Total of 12 sessions. 2 parallel arms (active and sham). Anode electrode over LDLPFC with Cathode electrode over RDLPFC.
Device: Device: 1x1 tDCS-CT with LTE and OLE headgear.
Outcome measure: Change in HDRS-17 at Week 6.
Results: Patients in the active tDCS arm showed significantly superior improvement compared to those in the sham arm (βint = -1.68; number needed to treat, 5.8; 95% CI, 3.3-25.8; P = .01). Cumulative response rates were higher in the active vs sham groups (67.6% vs 30.4%; number needed to treat, 2.69; 95% CI, 1.84-4.99; P = .01), but not remission rates (37.4% vs 19.1%; number needed to treat, 5.46; 95% CI, 3.38-14.2; P = .18). Adverse events, including treatment-emergent affective switches, were similar between groups, except for localized skin redness that was higher in the active group (54% vs 19%; P = .01).
Trial: Trial of Electrical Direct-Current Therapy versus Escitalopram for Depression. New England Journal of Medicine 2017.
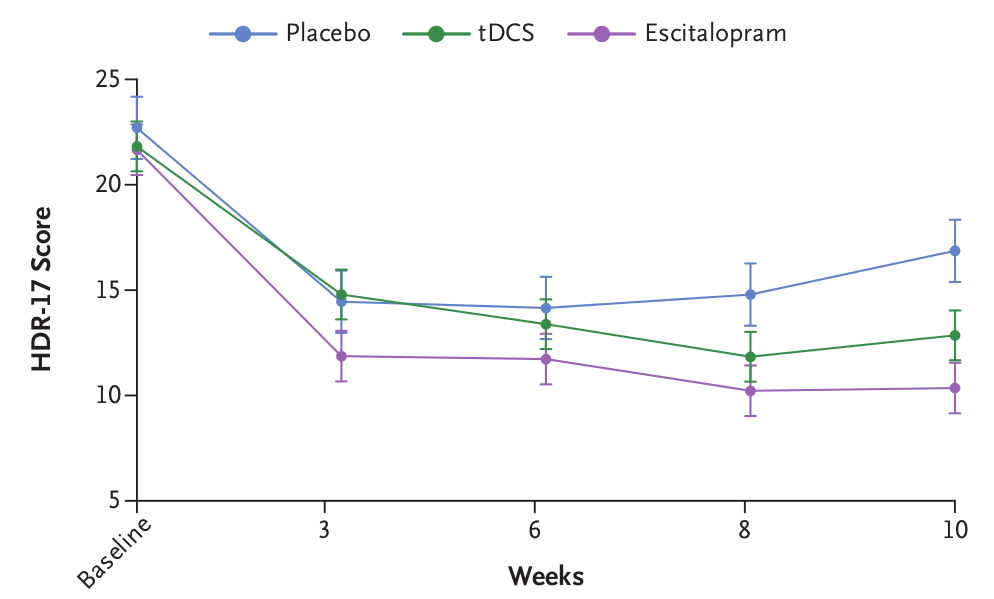
Design: Randomized, sham-controlled, double-blinded non-inferiority trial involving 245 patients aged between 18 to 75 years. Participants were diagnosed with unipolar depression, had HDRS-17 score >= 17 and were at low risk of suicide.
Intervention: 15 daily 30 minute sessions at 2 mA. Then 1 session every week until week 10. Total of 22 sessions. 3 parallel arms (drug + sham tDCS, active tDCS + oral placebo, sham tDCS+ oral placebo). Drug (escitalopram) was given at a dose of 10 mg per day for 3 weeks and 20 mg per day thereafter. Anode electrode over LDLPFC with Cathode electrode over RDLPFC using the OLE system.
Device: Soterix Medical 1X1 tDCS-CT with OLE headgear.
Outcome measure: Change in HDRS-17 from baseline to 10 weeks.
Results: In the intention-to-treat analysis, the mean (±SD) decrease in the score from baseline was 11.3±6.5 points in the drug group, 9.0±7.1 points in the tDCS group, and 5.8±7.9 points in the placebo group. The lower boundary of the confidence interval for the difference in the decrease for tDCS versus escitalopram (difference, -2.3 points; 95% confidence interval [CI], -4.3 to -0.4; P=0.69) was lower than the noninferiority margin of -2.75 (50% of placebo minus escitalopram), so noninferiority could not be claimed. Escitalopram and tDCS were both superior to placebo (difference vs. placebo, 5.5 points [95% CI, 3.1 to 7.8; P<0.001] and 3.2 points [95% CI, 0.7 to 5.5; P=0.01], respectively). Patients receiving tDCS had higher rates of skin redness, tinnitus, and nervousness than did those in the other two groups, and new-onset mania developed in 2 patients in the tDCS group. Patients receiving escitalopram had more frequent sleepiness and obstipation than did those in the other two groups.
The tDCS-LTE™ therapy is now approved in select countries for the treatment of Major Depression. If you are interested in trying tDCS-LTE™ for yourself or a loved one, please contact us online and a Soterix Medical representative will be in touch with you.